Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0308)
| Name |
Chebulagic Acid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Chebulagic acid; CHEBI:3583; 23094-71-5; 2-[(4R,5S,7R,25S,26R,29S,30S,31S)-13,14,15,18,19,20,31,35,36-Nonahydroxy-2,10,23,28,32-pentaoxo-5-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy-3,6,9,24,27,33-hexaoxaheptacyclo[28.7.1.04,25.07,26.011,16.017,22.034,38]octatriaconta-1(37),11,13,15,17,19,21,34(38),35-nonaen-29-yl]acetic acid; CHEMBL525240; NSC636590; 2-[nonahydroxy-pentaoxo-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy-[?]yl]acetic acid; C41-H30-O27; GN-29; BDBM50366290; E80601; Q5089009; .beta.-D-Glucopyranose, cyclic 3,6-[(1R)-4,4',5,5',6,6'-hexahydroxy[1,1'-biphenyl]-2,2'-dicarboxylate] 1-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate), cyclic
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Status |
Investigative
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Structure |
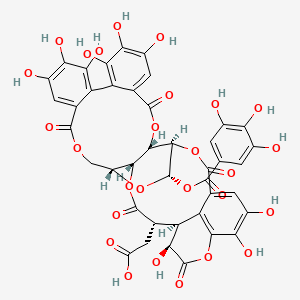 |
||||
|
3D MOL
|
|||||
| Formula |
C41H30O27
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
2-[(4R,5S,7R,25S,26R,29S,30S,31S)-13,14,15,18,19,20,31,35,36-nonahydroxy-2,10,23,28,32-pentaoxo-5-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy-3,6,9,24,27,33-hexaoxaheptacyclo[28.7.1.04,25.07,26.011,16.017,22.034,38]octatriaconta-1(37),11,13,15,17,19,21,34(38),35-nonaen-29-yl]acetic acid
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1C2C3C(C(C(O2)OC(=O)C4=CC(=C(C(=C4)O)O)O)OC(=O)C5=CC(=C(C6=C5C(C(C(=O)O3)CC(=O)O)C(C(=O)O6)O)O)O)OC(=O)C7=CC(=C(C(=C7C8=C(C(=C(C=C8C(=O)O1)O)O)O)O)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C41H30O27/c42-13-1-8(2-14(43)24(13)49)35(56)68-41-34-33-31(64-39(60)12(6-19(47)48)22-23-11(38(59)67-34)5-17(46)27(52)32(23)65-40(61)30(22)55)18(63-41)7-62-36(57)9-3-15(44)25(50)28(53)20(9)21-10(37(58)66-33)4-16(45)26(51)29(21)54/h1-5,12,18,22,30-31,33-34,41-46,49-55H,6-7H2,(H,47,48)/t12-,18+,22-,30-,31+,33-,34+,41-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
HGJXAVROWQLCTP-YABCKIEDSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Health | ICD-11: N.A. | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | rBMMSCs (Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells) | ||||
| In Vivo Model |
Sprague-Dawley rats (4 weeks) were obtained from the Animal Center of the Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine. Procurement, maintenance, and treatment of the animals were performed under the supervision of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of the Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine. The Gaussian 16 C.01 program was purchased from Guangzhou Molcalx Ltd. (Guangzhou, China).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Two hydrolyzable tannins, chebulagic acid and chebulinic acid, can act as natural ferroptosis inhibitors. Their ferroptosis inhibition is mediated by regular antioxidant pathways (ROS scavenging and iron chelation), rather than the redox-based catalytic recycling pathway exhibited by Fer-1. | ||||
