Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0270)
| Name |
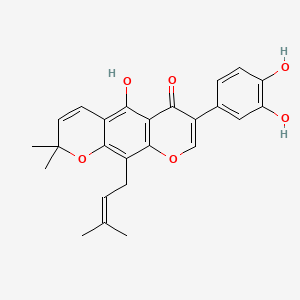
Auriculasin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AURICULASIN; 60297-37-2; Cudraisoflavone A; 7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-10-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-6-one; NSC285656; CHEMBL459129; DTXSID50418510; CHEBI:178564; HY-N2911; BDBM50442400; LMPK12050247; AKOS040761390; FS-8648; NSC 285656; NSC-285656; CS-0023510; 7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-10-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-2h,6h-pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-6-one; NCGC00384963-01!7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-10-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-6-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
 |
||||
| Formula |
C25H24O6
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-10-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)pyrano[3,2-g]chromen-6-one
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC(=CCC1=C2C(=C(C3=C1OC=C(C3=O)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)O)O)O)C=CC(O2)(C)C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H24O6/c1-13(2)5-7-16-23-15(9-10-25(3,4)31-23)21(28)20-22(29)17(12-30-24(16)20)14-6-8-18(26)19(27)11-14/h5-6,8-12,26-28H,7H2,1-4H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PSEBCAMYGWGJMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | ||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT 116 cells | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 cells | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response regulation | Auriculasin promoted the expression of Keap1 and AIFM1, but significantly reduced the phosphorylation level of AIFM1. AC can promote colorectal cancer cell apoptosis, ferroptosis and oxeiptosis by inducing ROS generation, thereby inhibiting cell viability, invasion and colony formation, indicating that AC has a significant tumor suppressor effect. | |||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | |||
| Responsed Disease | Colorectal cancer | ICD-11: 2B91 | ||
| Responsed Regulator | Apoptosis-inducing factor 1, mitochondrial (AIFM1) | Driver | ||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | |||
| Cell apoptosis | ||||
| Cell invasion | ||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT 116 cells | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0291 |
| SW480 cells | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0546 | |
| Response regulation | Auriculasin promoted the expression of Keap1 and AIFM1, but significantly reduced the phosphorylation level of AIFM1. AC can promote colorectal cancer cell apoptosis, ferroptosis and oxeiptosis by inducing ROS generation, thereby inhibiting cell viability, invasion and colony formation, indicating that AC has a significant tumor suppressor effect. | |||
