Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0090)
| Name |
Clioquinol
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
clioquinol; 130-26-7; 5-Chloro-7-iodoquinolin-8-ol; Iodochlorhydroxyquin; Chinoform; Chloroiodoquin; 5-Chloro-7-iodo-8-quinolinol; Chloroiodoquine; 5-Chloro-8-hydroxy-7-iodoquinoline; Vioform; Iodochloroxyquinoline; Cliquinol; Iodochlorohydroxyquinoline; Chlorojodochin; Enteroquinol; Iodochloroquine; Iodochloroxine; Iodoenterol; 7-Iodo-5-chloroxine; Entero-Vioform; Iodochlorhydroxyquinoline; 5-Chloro-7-iodo-8-hydroxyquinoline; Iodoxyquinoline; Alchloquin; Barquinol; Budoform; Cifoform; Dermaform; Dioquinol; Domeform; Eczecidin; Enteroseptol; Enterozol; Enterseptol; Entrokin; Iodenterol; Lekosept; Mycoquin; Quinambicide; Quinoform; Rheaform; Amebil; Amoenol; Bactol; Emaform; Nioform; Rometin; Entero-Bioform; Iodochlorohydroxyquin; Hi-Enterol; Iodochlorhydroxyquinol; Hydriodide-enterol; Quin-O-Creme; Chinoformum; Cliochinolum; Entero-Septol; Enterum locorten; 5-Chloro-7-iodo-quinolin-8-ol; Domeform-HC; 8-Quinolinol, 5-chloro-7-iodo-; 7-Iodo-5-chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline; Clioquinolum; Enterovalodon; Alioform; Chloro-8-hydroxyiodoquinoline; Enteritan; Jodchloroxychinolinum; Corque; Cortin; Oralcer; Iodo; Iodochloroxychinolinum; Cremo-quin; Entero-bio form; Entero-Vioformio; Ala-Quin; Quinoform (antiseptic); UAD Lotion; Vioform n.n.r.; Cliochinolo; Cliochinolo [DCIT]; Caswell No. 193; Formtone-HC; Clioquinolum [INN-Latin]; Quinoline, chloro-8-hydroxyiodo-; 5-Chlor-7-jod-8-hydroxy-chinolin; Rheaform boluses; iodochlorhydroxyquinolone; 5-Chlor-7-jod-8-hydroxy-chinolin [German]; NSC-3531; 7BHQ856EJ5; DTXSID7022837; CHEBI:74460; NSC-74938; NCGC00016391-05; CAS-130-26-7; TG2-36-2; C9H5ClINO; PBT-1; Quinoform (VAN); DTXCID502837; loquinol; Vioformio; Hi-eneterol; Iodochlorhydroxyquin Cream; Vioform-Hydrocortisone Mild; 22112-03-4; SMR000058282; Rheaform Boluses (Veterinary); CCRIS 6050; HSDB 6843; SR-01000002987; NSC 3531; EINECS 204-984-4; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 024001; BRN 0153637; UNII-7BHQ856EJ5; Linolasept; Clioquinol [USP:INN:BAN]; Cloquinol; AI3-16451; Clioquinol (CQ); component of Hyquin; MFCD00006787; NSC 74938; Nystaform (Salt/Mix); Clioquinol (USP/INN); CLIOQUINOL [INN]; component of Formtone-HC; component of Heb-Cort V; Prestwick0_000886; Prestwick1_000886; Prestwick2_000886; Prestwick3_000886; CLIOQUINOL [HSDB]; Formtone-HC (Salt/Mix); CLIOQUINOL [VANDF]; CHEMBL497; EC 204-984-4; cid_2788; CLIOQUINOL [MART.]; SCHEMBL3967; CLIOQUINOL [USP-RS]; CLIOQUINOL [WHO-DD]; NCIOpen2_009062; Oprea1_438281; BSPBio_000672; BSPBio_002466; 5-21-03-00294 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); ksc-8-192; MLS000069389; MLS002454410; SPECTRUM1505114; SPBio_002891; BPBio1_000740; CLIOQUINOL [ORANGE BOOK]; component of Hyquin (Salt/Mix); BDBM32188; IODOCHLORHYDROXYQUIN [MI]; CLIOQUINOL [EP MONOGRAPH]; NSC3531; WLN: T66 BNJ GG II JQ; CLIOQUINOL [USP MONOGRAPH]; HMS1570B14; HMS1648J07; HMS2093I12; HMS2097B14; HMS2230I20; HMS3372J20; HMS3714B14; KUC105859N; Pharmakon1600-01505114; component of Cort-Quin (Salt/Mix); Tox21_110416; Tox21_200291; NSC759822; NYSTAFORM COMPONENT CLIOQUINOL; s4601; STK399761; 5-chloro-8-hydroxy-7-iodo-quinoline; component of Heb-Cort V (Salt/Mix); AKOS000120779; Tox21_110416_1; AC-6792; CCG-213339; DB04815; FD10468; NSC-759822; CLIOQUINOL COMPONENT OF NYSTAFORM; SMP1_000073; IODOCHLORHYDROXYQUIN [GREEN BOOK]; NCGC00016391-01; NCGC00016391-02; NCGC00016391-03; NCGC00016391-04; NCGC00016391-06; NCGC00016391-07; NCGC00016391-08; NCGC00016391-09; NCGC00016391-10; NCGC00016391-13; NCGC00021665-03; NCGC00021665-04; NCGC00021665-05; NCGC00257845-01; S4601 5-Chloro-8-hydroxy-7-iodoquin; AS-14597; BC167259; HY-14603; SBI-0206782.P001; AB00384254; FT-0603209; 4-stearylamino-phenyl-trimethylam. metilsulf.; EN300-20836; A16461; Clioquinol, VETRANAL(TM), analytical standard; component of Vioform-Hydrocortisone (Salt/Mix); D03538; AB00384254_17; 5-Chloro-7-iodo-8-quinolinol, >=95.0% (HPLC); CU-01000000767-2; Q-200875; Q5134338; SR-01000002987-2; SR-01000002987-3; SR-01000002987-4; BRD-K09255212-001-04-2; Z104483432; Clioquinol, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard; Clioquinol, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Clindamycin phosphate, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only; Clioquinol, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; InChI=1/C9H5ClINO/c10-6-4-7(11)9(13)8-5(6)2-1-3-12-8/h1-4,13; CQL
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
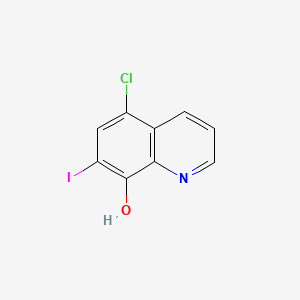 |
||||
| Formula |
C9H5ClINO
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
5-chloro-7-iodoquinolin-8-ol
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC2=C(C(=C(C=C2Cl)I)O)N=C1
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C9H5ClINO/c10-6-4-7(11)9(13)8-5(6)2-1-3-12-8/h1-4,13H
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QCDFBFJGMNKBDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 2 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease | ICD-11: 8A00 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1) | Suppressor | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | SK-N-SH cells | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0531 | |
| In Vivo Model |
In total, twelve healthy adult rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta lasiotis, aged 4-5 years, and weighed 3.5-5 kg at the start of the study) were obtained from Sichuan Primed Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Monkeys were randomly divided into two groups: normal (control) group (n = 3) and MPTP group (n = 9). Monkeys from MPTP group were administered with MPTP by intramuscular injection daily at the beginning of the study, and then the MPTP dose was gradually added to 0.5 mg/kg at the end of the experiment. Monkeys from control group were injected with saline instead, and the other conditions were the same with MPTP group.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Ferroptosis was probably involved in the pathogenesis of parkinson's disease (PD). Clioquinol (CQ) can decrease the excessive iron in the SN to normal level and directly protect DA neurons against oxidative stress probably by activating the AKT/mTOR survival pathway and blocking p53-medicated cell death. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Parkinson disease | ICD-11: 8A00 | |||
| Responsed Regulator | Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | Driver | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| In Vitro Model | SK-N-SH cells | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0531 | |
| In Vivo Model |
In total, twelve healthy adult rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta lasiotis, aged 4-5 years, and weighed 3.5-5 kg at the start of the study) were obtained from Sichuan Primed Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Monkeys were randomly divided into two groups: normal (control) group (n = 3) and MPTP group (n = 9). Monkeys from MPTP group were administered with MPTP by intramuscular injection daily at the beginning of the study, and then the MPTP dose was gradually added to 0.5 mg/kg at the end of the experiment. Monkeys from control group were injected with saline instead, and the other conditions were the same with MPTP group.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Ferroptosis was probably involved in the pathogenesis of parkinson's disease (PD). Clioquinol (CQ) can decrease the excessive iron in the SN to normal level and directly protect DA neurons against oxidative stress probably by activating the AKT/mTOR survival pathway and blocking p53-medicated cell death. | ||||
