Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0085)
| Name |
Carvedilol
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
carvedilol; 72956-09-3; Coreg; Dilatrend; Eucardic; Kredex; Carvedilolum [Latin]; Carvedilolum; Querto; BM 14190; 1-(9H-Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol; BM-14190; Dimitone; Artist; SKF 105517; 1-((9H-Carbazol-4-yl)oxy)-3-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)propan-2-ol; Coronis; Korvasan; Talliton; DQ 2466; 1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino]propan-2-ol; DQ-2466; (+-)-1-(Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-((2-(o-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)-2-propanol; (+/-)-Carvedilol-d4; CHEMBL723; NSC-758694; SK&F-105517; [3-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-2-hydroxypropyl][2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amine; BM 14.190; BM-14-190; BM-14.190; CHEBI:3441; C07AG02; 0K47UL67F2; SKF-105517; Carvedilol-methyl-d3; 1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-{[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino}propan-2-ol; Coropress; Dibloc; 1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[(2-{[2-(methyloxy)phenyl]oxy}ethyl)amino]propan-2-ol; SMR000449280; Artist (TN); Coreg (TN); HSDB 7044; SR-01000759289; UNII-0K47UL67F2; MFCD00869663; 1-(9H-Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-(2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino)propan-2-ol; EG-P042; (R)-BM 14190; MFCD00864692; Carvedilol - Bio-X; BM14190; Carvedilol [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Spectrum_001665; CARVEDILOL [MI]; CARVEDILOL [INN]; CARVEDILOL [JAN]; Spectrum2_001673; Spectrum3_001182; Spectrum4_000636; Spectrum5_001436; CARVEDILOL [HSDB]; CARVEDILOL [USAN]; CARVEDILOL [VANDF]; CARVEDILOL [MART.]; CARVEDILOL [USP-RS]; CARVEDILOL [WHO-DD]; SCHEMBL22293; GTPL551; KBioGR_001252; KBioSS_002145; MLS000758299; MLS000759508; MLS001424092; MLS006011886; SPBio_001885; Carvedilol (JP17/USP/INN); CARVEDILOL [ORANGE BOOK]; DTXSID8022747; SCHEMBL10082334; SCHEMBL13287211; BDBM25759; KBio2_002145; KBio2_004713; KBio2_007281; KBio3_002323; CARVEDILOL [EP MONOGRAPH]; (R)-1-[(4-Carbazolyl)oxy]-3-[[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-2-propanol; OGHNVEJMJSYVRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N; CARVEDILOL [USP MONOGRAPH]; HMS2051N03; HMS2089B09; HMS2093E12; HMS3261E15; HMS3269N11; HMS3393N03; HMS3413B14; HMS3655O14; HMS3677B14; HMS3715D15; HMS3750I15; HMS3884E12; Pharmakon1600-01504257; Carvedilol 1.0 mg/ml in Methanol; AMY40801; BCP23386; EX-A5746; HY-B0006; Tox21_500347; BBL029064; MFCD00869664; NSC758694; s1831; STK621453; AKOS005554967; Carvedilol, >=98% (HPLC), solid; AC-1641; BCP9000493; CCG-100917; CCG-207952; CS-1194; DB01136; KS-1037; LP00347; NC00167; NSC 758694; SB17441; SDCCGSBI-0206771.P002; 2-Propanol, 1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)-, (+-)-; NCGC00167832-01; NCGC00167832-02; NCGC00167832-03; NCGC00167832-04; NCGC00167832-19; NCGC00261032-01; BC164291; SY129821; SY283162; BCP0726000253; SBI-0206771.P001; C2260; FT-0603055; FT-0603057; FT-0652640; FT-0664397; SW197547-3; C06875; D00255; F19969; AB00639903-07; AB00639903-09; AB00639903_10; AB00639903_11; AB00639903_12; L001243; Q412534; Q-200801; SR-01000759289-5; SR-01000759289-6; SR-01000759289-9; BRD-A10977446-001-04-8; BRD-A10977446-001-05-5; BRD-A10977446-045-01-1; Z1515383337; Carvedilol, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Ethyl 2-(9-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)-9H-fluoren-9-yl)acetate; Carvedilol, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxy-phenoxy)-ethylamino]-propan-2-ol; Carvedilol, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; (+/-)-1-CARBAZOL-4-YLOXY)-3-((2-(O-METHOXYPHENOXY)ETHYL)AMINO)-2-PROPANOL; 1-(CARBAZOL-4-YLOXY)-3-((2-(O-METHOXY-PHENOXY)ETHYL)AMINO)-2-PROPANOL; Carvedilol for system suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; 107741-96-8; 2-PROPANOL, 1-(9H-CARBAZOL-4-YLOXY)-3-((2-(2-METHOXYPHENOXY)ETHYL)AMINO)-, (+/-)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
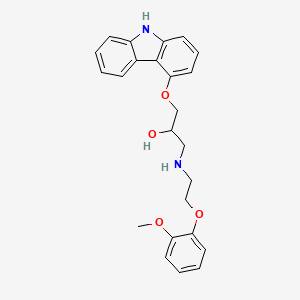 |
||||
| Formula |
C24H26N2O4
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino]propan-2-ol
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
COC1=CC=CC=C1OCCNCC(COC2=CC=CC3=C2C4=CC=CC=C4N3)O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H26N2O4/c1-28-21-10-4-5-11-22(21)29-14-13-25-15-17(27)16-30-23-12-6-9-20-24(23)18-7-2-3-8-19(18)26-20/h2-12,17,25-27H,13-16H2,1H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
OGHNVEJMJSYVRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 1 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Acute kidney failure | ICD-11: GB60 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| In Vitro Model | CHO-S/H9C2 cells | Normal | Cricetulus griseus | CVCL_A0TS | |
| NRK-49F cells | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_2144 | ||
| HK-2 cells | Normal | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0302 | ||
| C2C12 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0188 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0062 | ||
| NRK-52E cells | Normal | Rattus norvegicus | CVCL_0468 | ||
| LLC-PK1 cells | Normal | Sus scrofa | CVCL_0391 | ||
| PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | ||
| HT22 cells | Normal | Mus musculus | CVCL_0321 | ||
| hUPECs (Human urine-derived podocyte-like epithelial cells) | |||||
| In Vivo Model |
C57BL/6N male mice (CLEA Japan), aged 8-9 weeks, were used. AKI was induced by intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin solution (16 or 17 mg/kg as indicated; Nichi-Iko Pharmaceutical). Mice were orally treated with water only, promethazine (20 mg/kg in water), or rifampicin (20 mg/kg in 0.5% methylcellulose) every 12 hours for 4 days starting 30 minutes before the cisplatin injection, or orally treated with promethazine (20 mg/kg) in the following groups: (1) no promethazine, (2) pretreatment 30 minutes before cisplatin injection, (3) treatment from 30 minutes before injection to 24 hours after injection, (4) treatment from 24 to 96 hours after injection, and (5) treatment every 12 hours from 30 minutes before injection to 96 hours after injection.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Eight drugs and hormones that showed antiferroptotic activity, including omeprazole, indole-3-carbinol, rifampicin, promethazine, carvedilol, propranolol, estradiol, and triiodothyronine. Moreover, in mice, the drugs ameliorated acute kidney injury and liver injury, with suppression of tissue lipid peroxidation and decreased cell death. | ||||
