Ferroptosis-centered Drug Response Information
General Information of the Drug (ID: ferrodrug0065)
| Name |
Phenethyl isothiocyanate
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-Phenylethyl isothiocyanate; Phenethyl isothiocyanate; 2257-09-2; Phenylethyl isothiocyanate; (2-Isothiocyanatoethyl)benzene; Benzene, (2-isothiocyanatoethyl)-; PEITC; Phenylaethylsenfoel; 2-isothiocyanatoethylbenzene; ISOTHIOCYANIC ACID, PHENETHYL ESTER; PHENETHYLISOTHIOCYANATE; phenethyl-isothiocyanate; beta-Phenylethyl isothiocyanate; .beta.-Phenylethyl isothiocyanate; CHEBI:351346; NSC 87868; 2-phenylethylisothiocyanate; 6U7TFK75KV; beta-Phenethyl isothiocyanate; CHEMBL151649; .beta.-Phenethyl isothiocyanate; 1-Isothiocyanato-2-phenylethane; DTXSID5021120; NSC-87868; Isothiocyanic Acid 2-Phenylethyl Ester; JC-5411; MFCD00004821; Phenylaethylsenfoel [German]; 1-ISOTHIOCYANATO-2-PHENYLETHANE (1,1,2,2-D4); CCRIS 3146; EINECS 218-855-5; BRN 2084162; WLN: SCN2R; ss-Phenethyl isothiocyanate; Epitope ID:138724; UNII-6U7TFK75KV; 2-phenyl ethyl isothiocyanate; SCHEMBL156960; Phenethyl isothiocyanate, 99%; DTXCID901120; FEMA NO. 4014; IZJDOKYDEWTZSO-UHFFFAOYSA-; (2-Isothiocyanato-ethyl)-benzene; (2-Isothiocyanatoethyl)benzene #; 1-(2-isothiocyanatoethyl)benzene; 2-Phenylethyl isothiocyanate, FG; HMS1783C17; HMS3870G13; NSC87868; Tox21_200100; (2-Isothiocyanatoethyl)benzene, 9CI; BBL009999; BDBM50240850; JC5411; PHENETHYL ISOTHIOCYANATE [MI]; STK397325; AKOS000119469; DB12695; JC 5411; JC 5411JC-5411; NCGC00248526-01; NCGC00257654-01; PHENYLETHYL ISOTHIOCYANATE [FHFI]; AC-12769; AS-17373; BP-12941; HY-23155; NCI60_041942; CAS-2257-09-2; Isothiocyanic acid .beta.-phenylethyl ester; FT-0604634; P0986; Phenethyl isothiocyanate, analytical standard; EN300-17386; D92051; 4-12-00-02476 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); A816267; J-802164; Q7181339; W-107466; BRD-K56700933-001-02-1; Z56924472; F0001-0795; InChI=1/C9H9NS/c11-8-10-7-6-9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-5H,6-7H2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
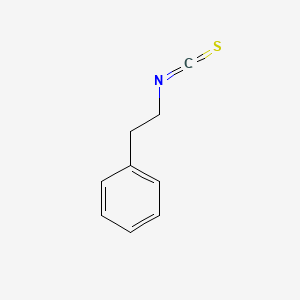 |
||||
| Formula |
C9H9NS
|
||||
| IUPAC Name |
2-isothiocyanatoethylbenzene
|
||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)CCN=C=S
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C9H9NS/c11-8-10-7-6-9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-5H,6-7H2
|
||||
| InChIKey |
IZJDOKYDEWTZSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Full List of Ferroptosis Target Related to This Drug
Unspecific Target
| In total 3 item(s) under this Target | |||||
| Experiment 1 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [1] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B51 | |||
| Pathway Response | Fatty acid metabolism | hsa01212 | |||
| Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | ||||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| In Vitro Model | K7M2-WT cells | Osteosarcoma | Mus musculus | CVCL_V455 | |
| In Vivo Model |
Male BALB/c mice, aged 4 weeks (14-16 g), were purchased from SPF (Beijing) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. K7M2 osteosarcoma cells were harvested and suspended in PBS at 4 . Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane. The left hindlimbs were shaved and cleaned with 75% ethanol. The knees of the mice were flexed beyond 90 and the cortex of the proximal tibial crest was penetrated using a 25 gauge needle by a rotating action. Once the tibial bone cortex was penetrated, the needles were further inserted 2 mm along the diaphysis, followed by injection of 10 uL of K7M2 osteosarcoma cells (5 x 105 cells) into the tibia.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Response regulation | Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) induces ferroptosis, autophagy, and apoptosis in K7M2 osteosarcoma cells by activating the ROS-related MAPK signaling pathway. | ||||
| Experiment 2 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [2] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Osteosarcoma | ICD-11: 2B51 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | ||||
| Autophagy | hsa04140 | ||||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell apoptosis | |||||
| Cell autophagy | |||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MNNG/HOS Cl #5 cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0439 | |
| U2OS cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0042 | ||
| MG-63 cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0426 | ||
| 143B cells | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_2270 | ||
| Response regulation | Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) reduced cell viability, inhibited proliferation, caused #REF!/M cell cycle arrest, altered iron metabolism, induced GSH depletion, generated ROS, activated MAPK signaling pathway, and triggered multiple cell death modalities, mainly ferroptosis, apoptosis, and autophagy, in human osteosarcoma cells. | ||||
| Experiment 3 Reporting the Ferroptosis-centered Drug Act on This Target | [3] | ||||
| Responsed Disease | Pancreatic cancer | ICD-11: 2C10 | |||
| Pathway Response | Ferroptosis | hsa04216 | |||
| Cell Process | Cell ferroptosis | ||||
| Cell proliferation | |||||
| In Vitro Model | MIA PaCa-2 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0428 | |
| PANC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_0480 | ||
| CFPAC-1 cells | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens | CVCL_1119 | ||
| Response regulation | The synergistic cell death induced by the combined treatment with Cotylenin A (CN-A) and phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) is mainly due to the induction of ferroptosis. Therefore, the combination of CN-A and PEITC has potential as a novel therapeutic strategy against pancreatic cancer. | ||||
References
